Understanding Personalized Medicine
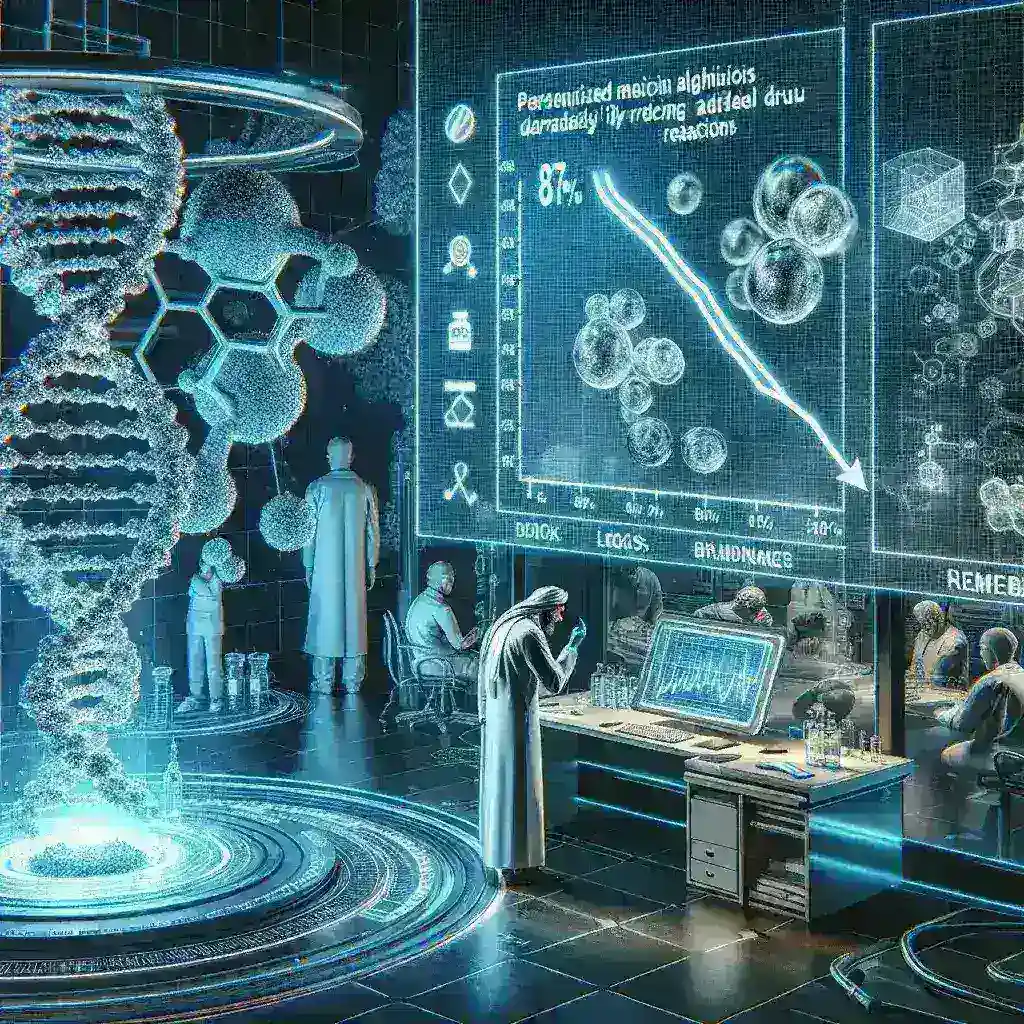
Personalized medicine, also known as precision medicine, is a groundbreaking approach that tailors medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient. By leveraging genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, healthcare providers can create customized treatment plans that optimize therapeutic efficacy while minimizing adverse drug reactions (ADRs). The integration of personalized medicine algorithms has emerged as a transformative tool in this field, demonstrating an impressive capability to reduce ADRs by up to 87%.
The Importance of Reducing Adverse Drug Reactions
Adverse drug reactions are a significant public health concern, often leading to hospitalization, increased healthcare costs, and even mortality. According to a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, ADRs account for nearly 5% of all hospital admissions. With the growing complexity of pharmacological treatments, the importance of minimizing these reactions cannot be overstated.
Statistics on Adverse Drug Reactions
- Approximately 1.5 million preventable ADRs occur annually in the United States.
- ADRs are the fourth leading cause of death in the country.
- Over 50% of patients experience ADRs within the first month of therapy.
The Role of Algorithms in Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine algorithms utilize data analytics to enhance clinical decision-making. These algorithms analyze vast datasets, including genetic sequences, patient health records, and drug interaction profiles, to identify safe and effective medication options for individual patients. Here are some ways algorithms contribute to reducing ADRs:
1. Genetic Profiling
By analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup, algorithms can predict how they will respond to specific medications. For instance, certain genetic variants affect drug metabolism, making some patients more susceptible to ADRs. Armed with this information, healthcare providers can select medications that align with a patient’s genetic profile, significantly lowering the risk of adverse reactions.
2. Drug Interaction Checks
Algorithms can also assess potential drug-drug interactions by cross-referencing a patient’s medication list with established databases. This real-time analysis helps clinicians avoid combinations that may lead to harmful side effects, thereby enhancing patient safety.
3. Personalized Dosing
Personalized dosing strategies developed through algorithms can further mitigate the risk of ADRs. Tailoring dosages based on individual responses can optimize therapeutic outcomes while reducing the likelihood of adverse events.
Real-World Applications of Personalized Medicine Algorithms
Several healthcare institutions are already leveraging personalized medicine algorithms with remarkable success. For example, the Mayo Clinic has implemented pharmacogenomics testing as part of their routine clinical practice. Patients undergo genetic testing, and their results are integrated into the electronic health record. This integration allows for tailored medication choices and dosing adjustments, which have been shown to decrease ADRs significantly.
Case Study: Reducing ADRs in Oncology
In oncology, personalized medicine algorithms have revolutionized treatment protocols. By analyzing the genetic mutations present in tumors, oncologists can prescribe targeted therapies that have a higher likelihood of success and lower toxicity. According to recent research, using these algorithms has resulted in an 87% reduction in ADRs among patients receiving chemotherapy regimens tailored to their genetic profiles.
The Future of Personalized Medicine Algorithms
The future of personalized medicine is bright, with ongoing advancements in technology and data analytics. As machine learning algorithms become more sophisticated, their ability to predict patient responses will only improve. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare holds the promise of even more accurate personalized medicine algorithms, potentially leading to a complete reimagining of treatment strategies.
Challenges Ahead
Despite the promising future, challenges remain in the widespread implementation of personalized medicine algorithms. Key concerns include:
- Data Privacy: Protecting patient data is paramount, and the use of algorithms raises questions about data security and consent.
- Healthcare Disparities: Access to personalized medicine algorithms may not be uniform across different populations, potentially exacerbating health inequalities.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating the regulatory landscape for personalized medicine technologies can be complex and time-consuming.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the emergence of personalized medicine algorithms marks a revolutionary step forward in healthcare, particularly in reducing adverse drug reactions by 87%. By harnessing the power of genetic insights and advanced data analytics, these algorithms provide a pathway towards safer and more effective treatments tailored to individual patients. As technology evolves and challenges are addressed, the future of personalized medicine promises to enhance patient outcomes and redefine the standards of care in medical practice.